Everything you need to know about Year 11 & 12 Biology
An overview of what the biology course entails for any student interested in the Sciences or a healthcare related field.
For students in Year 10, who may still be deciding what subjects to choose, this overview of the course will provide more information whether it is right for you.
Preliminary Biology
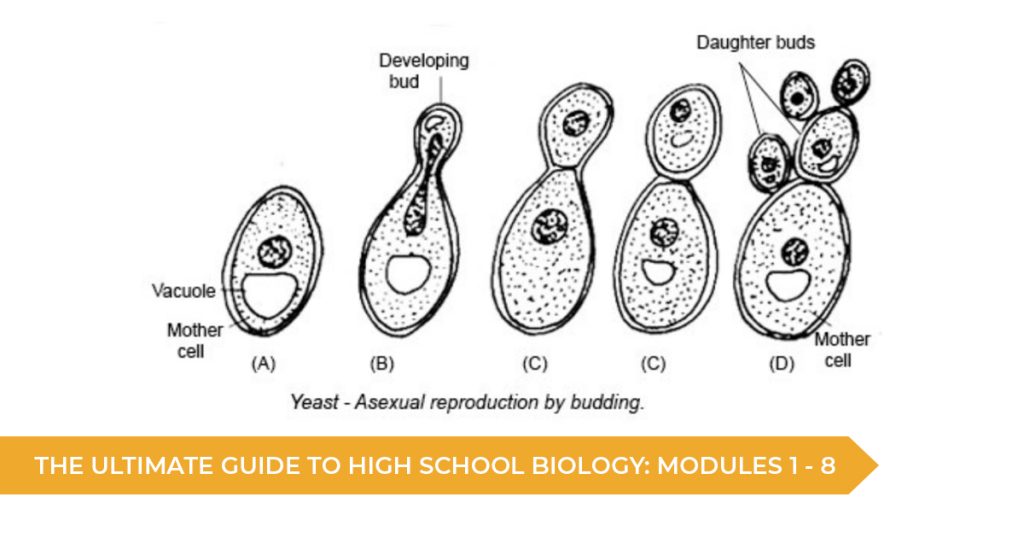
Module 1: Cells as the Basis of Life
This module focuses on the fundamental unit of living things: cells. You may be familiar with some of its content already from junior years, touching on the types of cells, the structures present, and how these cells are therefore able to function.
It covers the fundamental aspects of biology and provides foundational content which is built on in later modules.
Module 2: Organisation of Living Things
The focus of this module is on how living things are structured, with a focus on multicellular organisms. These organisms use various organs and systems in order to coordinate how a body functions, from nutrient and gas exchange via the lungs and gastrointestinal tract, to the transport of nutrients via the cardiovascular systems.
Module 3: Biological Diversity
Biodiversity is essential to balancing the Earth’s ecosystems. As such, the focus of this module is exploring what biodiversity, and what factors can affect it. The first section covers how environmental pressures, such as invasive species or agriculture, act as selective pressures on populations. The remainder focuses on the Theory of Evolution, specifically the process itself, different adaptations that have arisen, and what evidence supports this theory.
Module 4: Ecosystem Dynamics
The last module of the preliminary year brings all the previous topics together from a macroscopic approach. It looks at how populations and ecosystems interact and work together.
It builds on Module 3, using concepts such as evolution and biodiversity to explore how different factors can affect an ecosystem. Following this, past ecosystems are studied to observe how their ecosystems have been affected by such changes, and what adaptions have evolved as a result. Lastly, this understanding is extrapolated to future ecosystems, where students predict the role of humans on future biodiversity.
RELATED: How To Revise HSC Biology Before Trial Exams
HSC Biology
Module 5: Heredity
The first two modules of HSC Biology have a strong focus on genetics. Module 5 lays the foundational principles of genetics: what processes do species reproduce by and how do cells replicate.
It then covers the role of genetic material and its use in organisms for protein synthesis – a fundamental aspect of microbiology. Lastly, it explores how genes are inherited, and how these patterns of inheritance can be predicted in larger populations.
Module 6: Genetic Change
This module likewise follows on from Module 5, diving deeper into how genetic material can be altered. The first section explores mutations, its different types, causes and effects.
The second half of the module then analyses various genetic technologies. Some technologies in this module include cloning and genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and their impacts on biodiversity are further investigated.
Module 7: Infectious Disease
The last two modules are focused on disease, and have a stronger focus on human pathology. Module 7 is on infectious diseases specifically, and therefore the first section is on characterising how and what causes infectious diseases.
It then explores how organisms respond to infections – a complex battle between white blood cells and infectious agents. Lastly, it analyses how humans become immune to infection, and how processes, such as hand-washing, quarantine and vaccinations are used to prevent the spread of the disease.
Module 8: Non-Infectious Disease and Disorders
This last module focuses on what happens when normal processes of the body become deranged, i.e. the effects of the disease. Homeostasis is the way in which bodily functions are maintained, and the module first establishes how health is maintained during this period.
However, it then investigates how cancer, genetic or nutritional diseases can affect these processes.
The last section explores practical applications of biology via epidemiological studies, prevention of disease, and use of technologies such as dialysis, laser surgery in assisting those with disorders.
Need some extra help? We’ve got you covered at Talent 100
Our Sydney learning centres are open all week (Burwood, Chatswood, Epping, Hurstville & Sydney CBD), so you can brush-up on your Biology skills before exams start.
We also have online classes available for students in NSW – so you won’t miss out on any valuable Biology time this year! Take advantage of our 1-1 classes where you can get your past papers marked, ask questions about homework, or just speak to one of our HSC Chemistry Mentors.
Click here to find out more about our HSC Biology tuition courses.
Written by our Talent 100 HSC Chemistry Mentor, Judy Chen.




